6
back
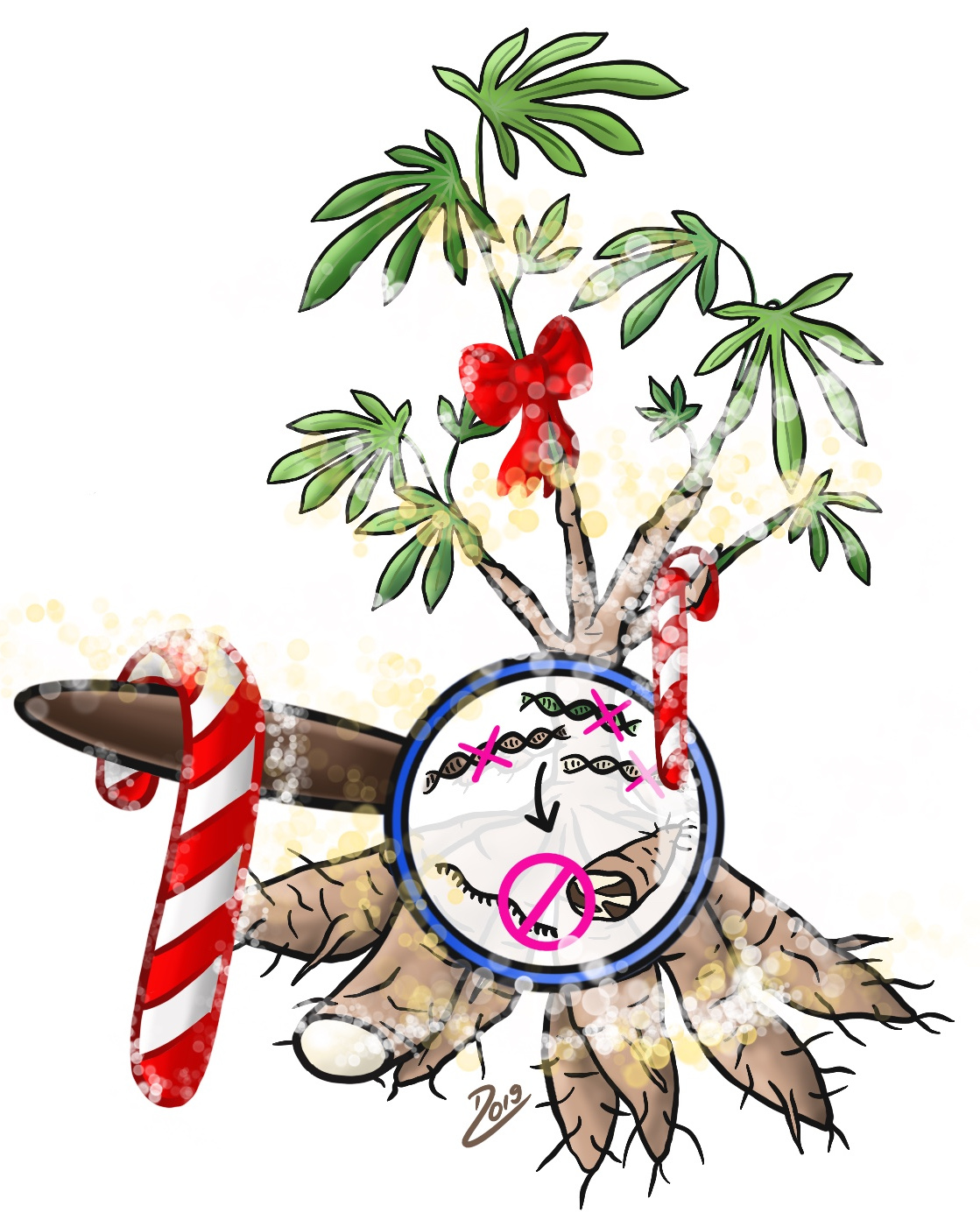


Crop: Cassava (Manihot esculenta)
Property: Resistance to CBSD virus
Manioc is an important staple food in African countries such as Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania and is cultivated in these countries by many small farmers. After maize, rice, wheat and potatoes, it is the most frequently cultivated crop in the world. In 2011, the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) warned against the spread of a plant virus that destroys large parts of the crop and thus the livelihoods of many. The virus is responsible for Cassava Brown Streak Disease (CBSD), which turns the manioc tuber brownish and inedible. The tricky thing about the disease is that the visible, aboveground parts of the plant do not show properties of the viral infection, and the damage only becomes visible after harvesting. In a work supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, researchers at the University of California succeeded in producing cassava plants with increased tolerance to brown stripe disease by eliminating several genes using CRISPR/Cas.
Publication
| Title | Simultaneous CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of cassava eIF4Eisoforms nCBP-1and nCBP-2reduces cassava brown streak disease symptom severity and incidence |  |
| Authors | Michael A. Gomez et al. | |
| Country | United States | |
| Journal | Plant Biotechnology Journal | |
| Year | 2018 | |
| DOI | doi:10.1111/pbi.12987 |
